
What is DNSSEC, and should I enable it?
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, ensuring the security and integrity of online communications has become paramount. One crucial component of this endeavor is the Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC), a suite of internet protocols designed to enhance the trustworthiness of the Domain Name System (DNS). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of DNSSEC, uncovering its mechanics, significance, and the compelling reasons why enabling it should be a priority for any organization operating online.
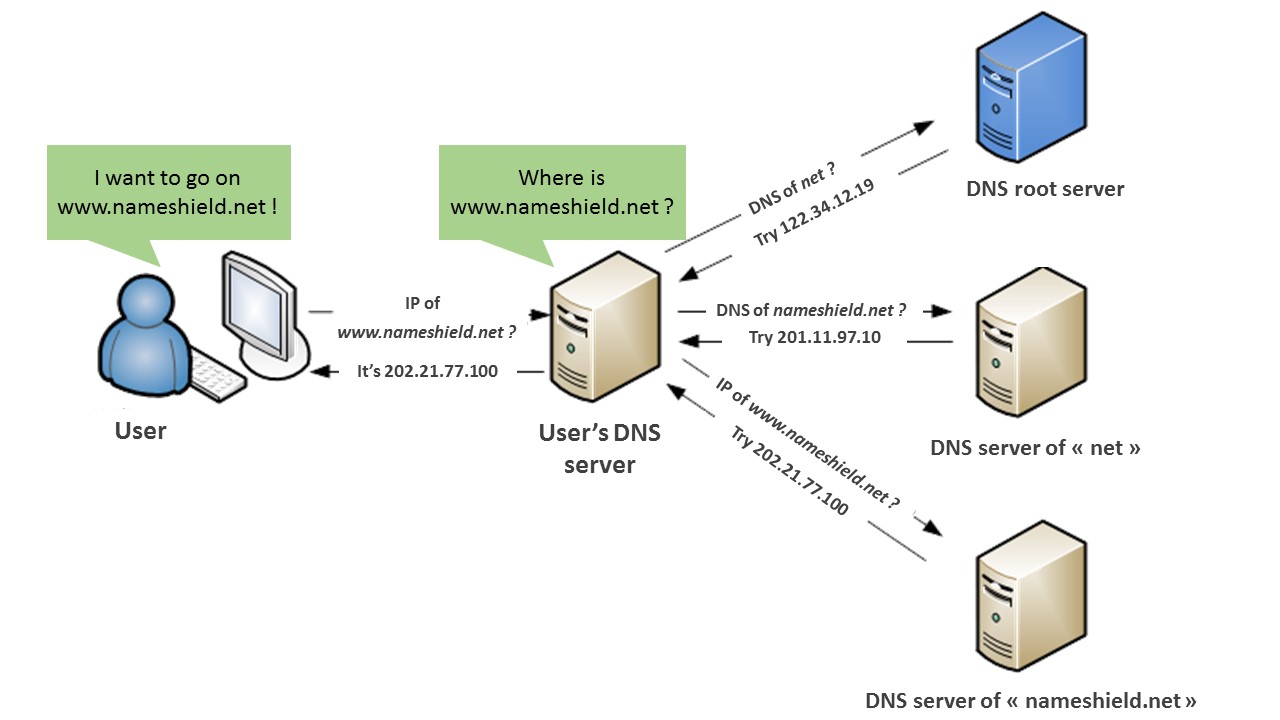
The DNS plays a pivotal role in translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses, enabling seamless navigation across the internet. However, this system is susceptible to various attacks, such as cache poisoning and man-in-the-middle scenarios, which can compromise the integrity of the information exchanged. DNSSEC aims to address these vulnerabilities by introducing a robust system of digital signatures and cryptographic keys, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of DNS data throughout its journey from the authoritative source to the end-user.
As we navigate the complexities of DNSSEC, we will explore its inner workings, the significance it holds in the realm of cybersecurity, and the multitude of benefits it offers. Furthermore, we will delve into the implementation process, addressing common misconceptions, and drawing insightful comparisons with IPv6, another pivotal technology shaping the future of the internet. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will possess a profound understanding of DNSSEC and be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to fortify your online presence against potential threats.
What is DNSSEC and how does it work?
DNSSEC, or Domain Name System Security Extensions, is a suite of internet protocols designed to enhance the security and integrity of the Domain Name System (DNS). At its core, DNSSEC employs a hierarchical system of digital signatures and cryptographic keys to authenticate the origin and validity of DNS data, ensuring that the information received by clients is accurate and unaltered.
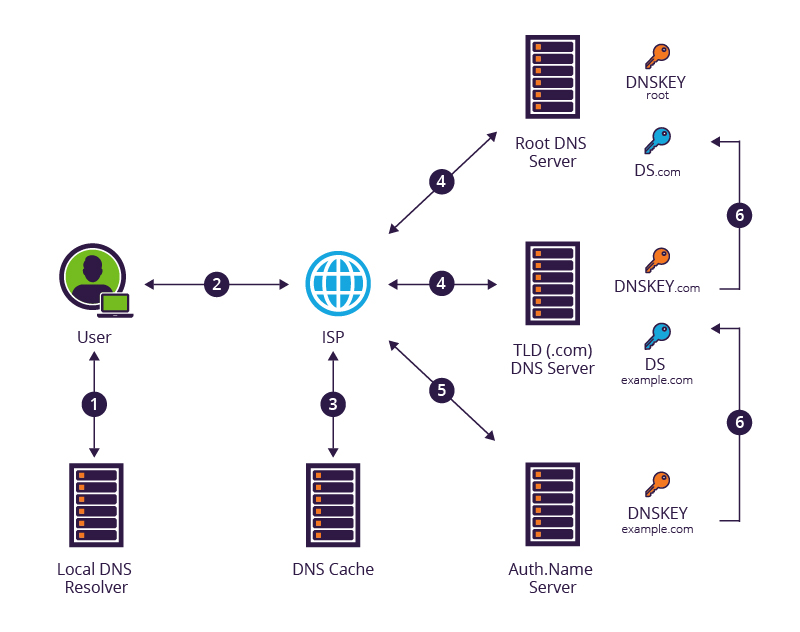
The mechanics of DNSSEC revolve around the concept of a chain of trust, which is established through a series of public-key cryptography operations. Each domain, starting from the root zone, possesses a unique cryptographic key pair consisting of a public and a private key. The private key is used to digitally sign the DNS records, while the corresponding public key is distributed and used for verification purposes.
When a client initiates a DNS query, the DNSSEC-enabled resolvers follow a specific sequence of steps:
Authentication: The resolver verifies the digital signature of the DNS response using the public key associated with the domain. If the signature is valid, it confirms that the data originated from an authorized source and has not been tampered with during transit.
Chain of Trust: The resolver then follows the chain of trust upwards, verifying the digital signatures at each level of the DNS hierarchy, ultimately reaching the root zone. This process ensures that the entire chain of DNS data is authenticated and trustworthy.
Data Integrity: If the digital signatures are successfully verified at all levels, the resolver can confidently deliver the requested DNS information to the client, knowing that it has not been compromised or manipulated.
DNSSEC leverages various cryptographic algorithms, such as RSA and ECDSA, to generate and manage the digital signatures and keys. These algorithms ensure the integrity and authenticity of the DNS data, while also providing a robust mechanism for key management and distribution.
Importance of DNSSEC in cybersecurity
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, DNSSEC plays a pivotal role in fortifying the integrity and trustworthiness of the internet's core infrastructure. The DNS, often referred to as the "phonebook of the internet," is a critical component that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, enabling seamless navigation and communication across the web.
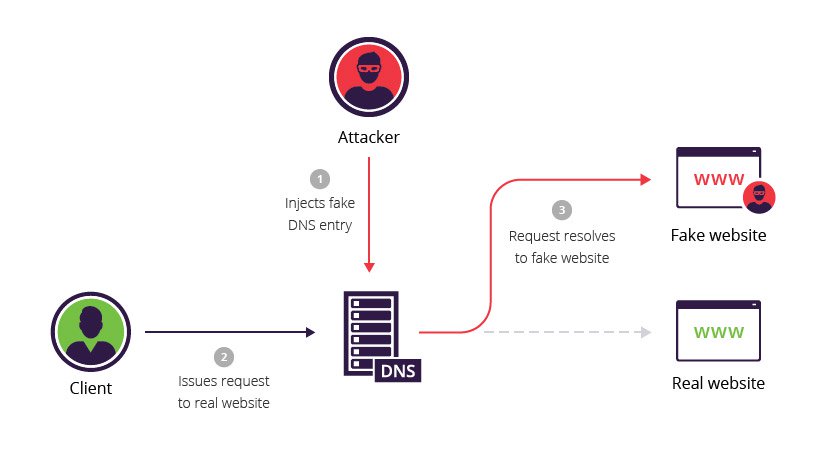
However, the traditional DNS system is susceptible to various attacks, such as cache poisoning and man-in-the-middle scenarios, which can compromise the integrity of the information exchanged. These vulnerabilities can lead to severe consequences, including redirecting users to malicious websites, facilitating phishing attacks, or enabling eavesdropping on sensitive communications.
By implementing DNSSEC, organizations can effectively mitigate these risks and enhance the overall security posture of their online presence. DNSSEC introduces a robust system of digital signatures and cryptographic keys, ensuring that the DNS data received by clients is authentic, unaltered, and originating from legitimate sources.
In the realm of cybersecurity, DNSSEC contributes to the following critical aspects:
Data Integrity: DNSSEC guarantees that the DNS information received by clients has not been tampered with or manipulated during transit, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks and cache poisoning attempts.
Authentication: Through the use of digital signatures and a chain of trust, DNSSEC authenticates the origin of DNS data, ensuring that it comes from authorized and legitimate sources, mitigating the risk of redirection to malicious websites or phishing attacks.
Confidentiality: While DNSSEC does not encrypt the DNS data itself, it establishes a foundation of trust that can be leveraged by other security protocols, such as DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT), to enhance confidentiality and prevent eavesdropping on sensitive communications.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries and regulatory bodies mandate the implementation of robust security measures to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure. DNSSEC can help organizations comply with these requirements by fortifying the integrity and authenticity of their online presence.
By embracing DNSSEC, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture, protect their digital assets, and safeguard their users from potential threats and malicious activities targeting the DNS infrastructure.
Benefits of enabling DNSSEC
Enabling DNSSEC on your domain and website offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond the realm of cybersecurity. By implementing this robust security protocol, you can unlock a range of advantages that not only fortify your online presence but also contribute to the overall trustworthiness and integrity of the internet ecosystem.
Enhanced Security and Trust: DNSSEC introduces a robust system of digital signatures and cryptographic keys, ensuring that the DNS data received by clients is authentic, unaltered, and originating from legitimate sources. This heightened level of security instills trust in your online presence, safeguarding your users from potential threats and malicious activities targeting the DNS infrastructure.
Mitigation of Cyber Threats: By implementing DNSSEC, you can effectively mitigate various cyber threats, such as cache poisoning, man-in-the-middle attacks, and DNS spoofing attempts. These threats can lead to severe consequences, including redirection to malicious websites, facilitation of phishing attacks, or enabling eavesdropping on sensitive communications.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Many industries and regulatory bodies mandate the implementation of robust security measures to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure. DNSSEC can help organizations comply with these requirements by fortifying the integrity and authenticity of their online presence, demonstrating a commitment to security best practices.
Improved User Experience: By ensuring the authenticity and integrity of DNS data, DNSSEC contributes to a seamless and reliable user experience. Users can navigate to your website with confidence, knowing that they are accessing the intended destination without the risk of being redirected to malicious or fraudulent sites.
Reputation and Brand Protection: In today's digital landscape, reputation and brand trust are invaluable assets. By implementing DNSSEC, you demonstrate a proactive approach to cybersecurity and a commitment to protecting your users' interests. This can enhance your brand's reputation and foster trust among your customer base.
Future-Proofing: As the internet continues to evolve and new threats emerge, DNSSEC provides a robust foundation for future security enhancements and protocols. By embracing DNSSEC today, you position your organization to adapt and stay ahead of emerging cybersecurity challenges.
Enabling DNSSEC is not only a prudent security measure but also a strategic investment in the long-term integrity and trustworthiness of your online presence. By leveraging this powerful security protocol, you can unlock a range of benefits that extend beyond cybersecurity, contributing to a more secure and reliable internet ecosystem for all.
DNSSEC implementation process
Implementing DNSSEC on your domain and website is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution. While the specific steps may vary depending on your infrastructure and hosting environment, the following general guidelines outline the key stages of the DNSSEC implementation process:
Preparation and Planning:
- Assess your current DNS infrastructure and identify any potential compatibility issues or required upgrades.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and stakeholder communication strategies.
- Ensure that all necessary personnel are trained and equipped with the required knowledge and tools.
Key Generation and Management:
- Generate a cryptographic key pair (public and private keys) for your domain using industry-standard algorithms, such as RSA or ECDSA.
- Securely store and manage the private key, as it is crucial for digitally signing your DNS records.
- Distribute the public key through the appropriate channels, such as DNS zone files and the DNSSEC trust chain.
DNS Zone Signing:
- Configure your DNS server or hosting provider to enable DNSSEC zone signing.
- Sign your DNS zone data using the private key generated in the previous step.
- Include the necessary DNSSEC resource records (e.g., RRSIG, DNSKEY, and NSEC/NSEC3) in your zone files.
Trust Anchor Submission:
- Submit your public key (also known as the Delegation Signer or DS record) to the parent zone or registrar for inclusion in the DNSSEC trust chain.
- This step establishes the chain of trust and allows resolvers to validate the authenticity of your DNS records.
Testing and Verification:
- Thoroughly test and verify the DNSSEC implementation using various tools and techniques, such as dig, drill, and online DNSSEC validators.
- Ensure that DNSSEC is properly configured and that the chain of trust is intact from the root zone down to your domain.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Implement regular monitoring and maintenance procedures to ensure the continued validity and integrity of your DNSSEC implementation.
- Periodically re-sign your DNS zones and update your keys to maintain optimal security levels.
- Stay informed about updates, vulnerabilities, and best practices related to DNSSEC and DNS security.
Throughout the implementation process, it is crucial to maintain close collaboration with your hosting provider, registrar, and any relevant stakeholders. Additionally, consulting with cybersecurity professionals or seeking guidance from industry resources can help ensure a smooth and successful DNSSEC deployment.
While the initial setup may require some effort and resources, the long-term benefits of DNSSEC in terms of enhanced security, trust, and compliance make it a worthwhile investment for any organization operating online.
Common misconceptions about DNSSEC
Despite the increasing adoption and awareness of DNSSEC, several misconceptions and myths surrounding this security protocol persist. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial to facilitate a better understanding and encourage wider implementation of DNSSEC across various domains and websites.
Misconception: DNSSEC is complex and difficult to implement. Reality: While the underlying mechanisms of DNSSEC involve cryptographic concepts and digital signatures, the implementation process has been streamlined and simplified over time. Many hosting providers and domain registrars now offer DNSSEC as a built-in feature, reducing the complexity for website owners and administrators.
Misconception: DNSSEC slows down DNS resolution and website performance. Reality: The impact of DNSSEC on DNS resolution and website performance is negligible in most cases. The additional overhead introduced by digital signatures and cryptographic operations is minimal, especially with modern hardware and optimized implementations.
Misconception: DNSSEC is only necessary for large organizations or critical infrastructure. Reality: DNSSEC is beneficial for websites and domains of all sizes, as it enhances the overall security and trustworthiness of the internet ecosystem. Even small businesses and personal websites can benefit from the added protection against DNS-based attacks and potential redirection to malicious sites.
Misconception: DNSSEC is a complete solution for DNS security. Reality: While DNSSEC significantly enhances the integrity and authenticity of DNS data, it does not provide a comprehensive solution for all DNS-related security concerns. It primarily focuses on preventing data manipulation and ensuring the validity of DNS responses. Additional measures, such as DNS filtering, rate limiting, and secure protocols like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT), may be required to address other security risks.
Misconception: DNSSEC is not widely adopted or supported. Reality: DNSSEC adoption has been steadily increasing over the years, with major internet service providers, registrars, and organizations embracing this security protocol. Many top-level domains (TLDs) and root servers have already implemented DNSSEC, and support for DNSSEC is widely available in modern DNS software and resolvers.
By addressing these misconceptions, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing DNSSEC and contribute to a more secure and trustworthy internet ecosystem. It is essential to separate fact from fiction and rely on authoritative sources and industry best practices when evaluating the suitability and benefits of DNSSEC for your specific requirements.
DNSSEC vs IPv6: Understanding the differences
While DNSSEC and IPv6 are both integral components of the modern internet infrastructure, they serve distinct purposes and address different aspects of security and functionality. Understanding the differences between these two technologies is crucial for organizations and individuals seeking to enhance their online presence and security posture.
Purpose:
- DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is a suite of internet protocols designed to enhance the security and integrity of the Domain Name System (DNS). Its primary goal is to ensure the authenticity and validity of DNS data through the use of digital signatures and cryptographic keys.
- IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the successor to IPv4, the current standard for internet addressing and routing. Its primary purpose is to address the depletion of IPv4 addresses and provide a larger address space, along with improved security features and enhanced support for emerging technologies.
Security Aspects:
- DNSSEC focuses specifically on securing the DNS infrastructure by verifying the authenticity and integrity of DNS data. It does not directly address confidentiality or encryption of DNS traffic.
- IPv6 includes built-in security features such as IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), which provides end-to-end encryption and authentication for IP communications. It also supports better access control and network segregation through improved addressing and routing capabilities.
Implementation and Deployment:
- DNSSEC is implemented at the DNS server level and requires coordination between domain owners, registrars, and internet service providers (ISPs) to establish a chain of trust.
- IPv6 deployment involves upgrading network infrastructure, devices, and applications to support the new protocol. It requires coordination between internet service providers, network equipment vendors, and end-user devices.
Compatibility and Interoperability:
- DNSSEC is designed to be backward-compatible with the existing DNS infrastructure. However, both DNSSEC-enabled and non-DNSSEC-enabled systems can coexist, with the latter potentially being more vulnerable to DNS-based attacks.
- IPv6 is not directly compatible with IPv4, and various transition mechanisms (e.g., dual-stack, tunneling, translation) are required to ensure interoperability between IPv4 and IPv6 networks during the migration process.
Scope and Impact:
- DNSSEC focuses specifically on securing the DNS infrastructure, which is a critical component of the internet's addressing and navigation system.
- IPv6 has a broader impact, affecting various aspects of networking, including addressing, routing, security, and the ability to support emerging technologies and applications.
While DNSSEC and IPv6 serve different purposes, they are both essential components of a secure and robust internet infrastructure. Organizations and individuals should consider implementing both technologies to enhance their overall security posture and prepare for the future of the internet.
How to enable DNSSEC on your website
Enabling DNSSEC on your website is a crucial step towards enhancing the security and trustworthiness of your online presence. By implementing this robust security protocol, you can ensure the authenticity and integrity of your DNS data, mitigating the risk of DNS-based attacks and protecting your users from potential threats. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you enable DNSSEC on your website:
Assess Your Current DNS Infrastructure:
- Identify your current DNS hosting provider or the platform where your DNS records are managed.
- Ensure that your provider supports DNSSEC and offers the necessary tools or interfaces for configuration.
Generate Cryptographic Keys:
- Generate a cryptographic key pair (public and private keys) using industry-standard algorithms, such as RSA or ECDSA.
- Follow your provider's guidelines or use specialized tools like dnssec-keygen to create the key pair.
- Securely store and manage the private key , as it is crucial for digitally signing your DNS records and maintaining the chain of trust.
Configure DNS Zone Signing:
- Log in to your DNS management interface or control panel provided by your hosting provider.
- Locate the DNSSEC settings or options to enable zone signing.
- Upload or paste the public key generated in the previous step.
- Configure the appropriate signing algorithms and key management settings according to your provider's guidelines.
Generate and Publish DNSSEC Records:
- Once zone signing is enabled, your DNS provider will automatically generate the necessary DNSSEC resource records, such as RRSIG (Resource Record Signature), DNSKEY, and NSEC/NSEC3.
- These records will be published in your DNS zone, allowing DNSSEC-enabled resolvers to validate the authenticity of your DNS data.
Submit Trust Anchor to Parent Zone:
- Your DNS provider will provide you with a Delegation Signer (DS) record, which is essentially a hash or digest of your public key.
- Submit this DS record to the parent zone or registrar, usually through their respective interfaces or processes.
- This step establishes the chain of trust and allows resolvers to validate the authenticity of your DNS records.
Test and Verify DNSSEC Implementation:
- Use various tools and online validators to test and verify the successful implementation of DNSSEC on your domain.
- Popular tools include dig, drill, and online DNSSEC validators provided by organizations like Internet.nl or DNSViz.
- Ensure that the DNSSEC records are present, the chain of trust is intact, and the digital signatures are valid.
Monitor and Maintain DNSSEC Configuration:
- Implement regular monitoring and maintenance procedures to ensure the continued validity and integrity of your DNSSEC implementation.
- Periodically re-sign your DNS zones and update your keys to maintain optimal security levels.
- Stay informed about updates, vulnerabilities, and best practices related to DNSSEC and DNS security.
It's important to note that the specific steps and interfaces may vary depending on your DNS hosting provider or platform. Consult your provider's documentation or seek assistance from their support team if you encounter any issues or have specific questions during the DNSSEC implementation process.
By enabling DNSSEC on your website, you are taking a proactive step towards enhancing the security and trustworthiness of your online presence, protecting your users from potential threats, and contributing to a more secure and reliable internet ecosystem.
Tools and techniques to verify DNSSEC implementation
Verifying the successful implementation of DNSSEC is a crucial step in ensuring the integrity and authenticity of your DNS data. Several tools and techniques are available to help you validate your DNSSEC configuration and identify potential issues or vulnerabilities. Here are some popular tools and techniques you can use to verify your DNSSEC implementation:
Command-line Tools
dig (Domain Information Groper): This versatile command-line tool is widely used for querying DNS servers and can be leveraged to verify DNSSEC implementation. By using the +dnssec and +cd options, you can request DNSSEC-related information and check for the presence of RRSIG (Resource Record Signature) records, which indicate DNSSEC signing. drill: Similar to dig, drill is another command-line tool specifically designed for DNSSEC testing and verification. It provides detailed output and can be used to trace the chain of trust from the root zone down to your domain.
Online DNSSEC Validators
Internet.nl DNSSEC Validator: This online tool provided by Internet.nl allows you to enter your domain and perform a comprehensive DNSSEC validation check. It displays detailed information about the DNSSEC records, chain of trust, and any potential issues or vulnerabilities. DNSViz: Developed by the DNSSEC Deployment Initiative, DNSViz is a web-based tool that visualizes the DNSSEC authentication chain for a given domain. It provides a graphical representation of the trust relationships and can help identify potential weaknesses or misconfigurations.
DNS Monitoring and Reporting Services
DNSMon: This service continuously monitors your DNS infrastructure, including DNSSEC implementation, and provides real-time alerts and reports on any issues or anomalies detected. DNS Observatory: Offered by the Internet Society, DNS Observatory is a free service that performs regular scans and provides detailed reports on your DNSSEC deployment, including potential vulnerabilities and best practice recommendations.
Zone File Analysis Tools
ZoneInspector: This tool analyzes your DNS zone files and checks for DNSSEC compliance, identifying potential issues such as missing or incorrect DNSSEC records, key management problems, or configuration errors. DNSViz Zone Scanner: Similar to the web-based version, the DNSViz Zone Scanner is a command-line tool that analyzes your DNS zone files and generates detailed reports on the DNSSEC authentication chain and potential vulnerabilities.
Network Packet Capture and Analysis
Wireshark: This versatile network protocol analyzer can be used to capture and analyze DNS traffic, including DNSSEC-related packets. By filtering and inspecting the captured packets, you can verify the presence of DNSSEC records and validate the digital signatures. tcpdump: A command-line packet capture tool that can be used in conjunction with dig or drill to analyze the DNS traffic and DNSSEC implementation.
It's important to note that while these tools and techniques can provide valuable insights into your DNSSEC implementation, they should be used in conjunction with regular monitoring and maintenance procedures. Additionally, consulting with cybersecurity professionals or seeking guidance from industry resources can help ensure a comprehensive and effective DNSSEC deployment strategy.
DNSSEC deployment challenges and solutions
While the implementation of DNSSEC offers numerous benefits in terms of enhancing the security and trustworthiness of the internet's core infrastructure, it is not without its challenges. Organizations and individuals embarking on a DNSSEC deployment journey may encounter various obstacles and hurdles along the way. In this section, we will explore some of the common challenges associated with DNSSEC deployment and provide practical solutions to overcome them.
Complexity and Technical Expertise
Challenge: DNSSEC involves cryptographic concepts, digital signatures, and a hierarchical chain of trust, which can be complex for those without specialized technical expertise. Solution: Leverage educational resources, training programs, and industry best practices to upskill your team. Additionally, consider partnering with experienced cybersecurity professionals or managed service providers who can guide you through the DNSSEC implementation process.
Legacy Infrastructure and Compatibility Issues
Challenge: Older DNS software, hardware, and network infrastructure may not be compatible with DNSSEC, potentially causing compatibility issues or performance degradation. Solution: Conduct a thorough assessment of your existing infrastructure and identify any potential compatibility issues. Plan for upgrades or replacements as necessary, and ensure that your DNSSEC deployment aligns with your overall infrastructure modernization roadmap.
Key Management and Rollover Processes
Challenge: Proper key management and periodic key rollovers are essential for maintaining the security and integrity of DNSSEC. However, these processes can be complex and error-prone if not handled correctly. Solution: Implement robust key management policies and procedures, including secure key generation, storage, and distribution mechanisms. Automate key rollover processes where possible, and ensure that your team is trained in best practices for key management.
Trust Anchor Distribution and Chain of Trust
Challenge: Establishing and maintaining the chain of trust from the root zone down to your domain can be challenging, particularly when dealing with multiple registrars, hosting providers, and parent zones. Solution: Closely collaborate with all stakeholders involved in the DNSSEC deployment process, including registrars, hosting providers, and parent zones. Follow established procedures for submitting and updating trust anchors (DS records), and regularly verify the integrity of the chain of trust.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Challenge: Effective monitoring and incident response mechanisms are crucial for detecting and mitigating potential DNSSEC-related issues or attacks. Solution: Implement robust monitoring solutions that can detect anomalies, misconfigurations, or potential attacks targeting your DNSSEC implementation. Develop incident response plans and procedures to address any identified issues promptly and effectively.
Organizational Buy-in and Resource Allocation
Challenge: Securing buy-in and allocating adequate resources (financial, human, and technical) for DNSSEC deployment can be a challenge, especially for organizations with limited budgets or competing priorities. Solution: Clearly communicate the benefits and importance of DNSSEC to stakeholders, highlighting its role in enhancing cybersecurity, compliance, and overall trust in your online presence. Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that aligns with your organization's strategic objectives and budget constraints.
By proactively addressing these challenges and implementing appropriate solutions, organizations can overcome the hurdles associated with DNSSEC deployment and reap the benefits of a more secure and trustworthy internet infrastructure.
Future of DNSSEC and emerging trends
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the need for robust security measures and trustworthy online communications becomes increasingly paramount. DNSSEC, with its ability to ensure the integrity and authenticity of DNS data, plays a crucial role in fortifying the internet's core infrastructure. However, the future of DNSSEC is not static, and various emerging trends and developments are shaping its evolution and adoption.
Widespread Adoption and Mandates
- The adoption of DNSSEC is gaining momentum, with more organizations, governments, and regulatory bodies recognizing its importance in enhancing cybersecurity and protecting critical infrastructure.
- Mandates and regulations requiring DNSSEC implementation are likely to become more prevalent, driving further adoption across various sectors and industries.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
- As new technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks, and edge computing gain traction, the need for secure and trustworthy DNS resolution becomes even more critical.
- DNSSEC will play a vital role in ensuring the integrity and authenticity of DNS data in these emerging ecosystems, enabling secure communication and data exchange.
Automation and Streamlined Deployment
- The deployment and management of DNSSEC are expected to become more streamlined and automated, reducing the complexity and overhead associated with implementation. 2.Tools and platforms that simplify key management, zone signing, and trust anchor distribution will continue to evolve, making DNSSEC more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Convergence with Other Security Protocols
- DNSSEC is likely to converge with other security protocols and technologies, such as DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT), to provide a comprehensive solution for secure and private DNS resolution.
- This convergence will enhance the overall security posture of online communications and enable organizations to leverage multiple layers of protection.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
- With the advent of quantum computing, traditional cryptographic algorithms may become vulnerable to attacks from powerful quantum computers.
- The development and integration of quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms into DNSSEC will be crucial to maintain its security and effectiveness in the face of this emerging threat.
Increased Focus on Monitoring and Incident Response
- As DNSSEC adoption grows, so will the need for robust monitoring and incident response mechanisms to detect and mitigate potential attacks or misconfigurations.
- Advanced monitoring tools, threat intelligence sharing, and collaborative incident response strategies will become increasingly important in the DNSSEC ecosystem.
The future of DNSSEC is inextricably linked to the evolving landscape of cybersecurity and the internet's core infrastructure. By staying ahead of emerging trends and embracing innovative solutions, organizations can position themselves at the forefront of DNSSEC adoption, ensuring a more secure and trustworthy online experience for themselves and their users.
FAQ on What is DNSSEC, and should I enable it?

DNSSEC stands for Domain Name System Security Extensions. It is a suite of protocols designed to add a layer of security to the Domain Name System (DNS) by enabling DNS responses to be verified and authenticated, thus protecting against various types of attacks.
DNSSEC works by adding digital signatures to DNS data. These signatures are created using cryptographic keys and can be verified by DNS resolvers to ensure that the data has not been altered or forged. The process relies on a chain of trust starting from the DNS root zone down to individual domain names.
- Enhanced Security: Protects against DNS spoofing, cache poisoning, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Data Integrity: Ensures that the data received has not been tampered with.
- Trustworthiness: Helps establish trust in the DNS infrastructure by validating the authenticity of DNS responses.
- Complexity: Requires careful planning and management of cryptographic keys.
- Performance Overhead: Can increase DNS response sizes and introduce additional latency.
- Compatibility: Not all DNS resolvers and infrastructure support DNSSEC, which can lead to compatibility issues.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your DNS hosting provider supports DNSSEC.
- Generate Keys: Create a Key Signing Key (KSK) and Zone Signing Key (ZSK) for your domain.
- Sign Your Zone: Sign your DNS records with the private key.
- Publish Public Keys: Publish the DNSKEY and DS records in your DNS zone.
- Parent Zone Delegation: Update the parent zone with your DS records to establish the chain of trust.
A chain of trust in DNSSEC is a hierarchical system of verification where each DNS zone (starting from the root) signs the zone below it. This creates a continuous trust path from the root zone down to the individual domain names, ensuring that DNS responses are authentic and have not been tampered with.
Yes, DNSSEC can increase the size of DNS responses due to the additional cryptographic signatures and keys. This can lead to higher latency and more frequent use of TCP instead of UDP for DNS queries. However, modern DNS infrastructure and optimizations, such as EDNS0, help mitigate these impacts.
Key rotation frequency can vary depending on your security policy. Generally, Zone Signing Keys (ZSKs) are rotated more frequently (e.g., annually or biannually), while Key Signing Keys (KSKs) are rotated less frequently (e.g., every few years). Automated tools can assist with key management and rotation.
While DNSSEC significantly enhances the security of DNS by preventing many types of attacks (such as DNS cache poisoning and spoofing), it does not protect against all attacks. For example, it does not encrypt DNS queries and responses, so it does not protect against eavesdropping.
DNSSEC adoption has been growing, with many top-level domains (TLDs) and a significant number of second-level domains implementing it. However, adoption varies, and not all resolvers and networks fully support DNSSEC yet. Continued awareness and advancements in DNSSEC tools are expected to drive further adoption.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, where cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, DNSSEC stands as a robust and essential defense mechanism for safeguarding the integrity and authenticity of online communications. By implementing this suite of internet protocols, organizations can fortify the trustworthiness of their online presence, mitigate the risk of DNS-based attacks, and contribute to a more secure internet ecosystem.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored the intricacies of DNSSEC, delving into its mechanics, significance, and the compelling benefits it offers. From enhancing data integrity and authentication to fostering compliance and regulatory adherence, the advantages of enabling DNSSEC are manifold.
While the implementation process may present challenges, such as complexity, legacy infrastructure compatibility, and key management, we have provided practical solutions and best practices to overcome these hurdles. By leveraging educational resources, collaborating with industry experts, and implementing robust monitoring and incident response mechanisms, organizations can navigate the DNSSEC deployment journey with confidence.
As we look towards the future, the adoption of DNSSEC is poised to gain further momentum, driven by emerging trends, technological advancements, and increasing regulatory mandates. The integration of DNSSEC with emerging technologies, the development of quantum-resistant cryptography, and the convergence with other security protocols will shape the evolution of this critical security measure.
In conclusion, enabling DNSSEC is not merely a cybersecurity best practice; it is a strategic investment in the long-term integrity and trustworthiness of your online presence. By embracing this powerful security protocol, you can unlock a range of benefits that extend beyond cybersecurity, contributing to a more secure and reliable internet ecosystem for all. To ensure the security and integrity of your online presence, consider enabling DNSSEC on your website today. Our team of cybersecurity experts is here to guide you through the implementation process, addressing any challenges or concerns you may have. Contact us now to take the first step towards fortifying your digital assets and safeguarding your users from potential threats. Don't wait – protect your online presence with DNSSEC and stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.





