What are the best practices for managing WordPress media files?
Effective management of media files in WordPress is crucial for maintaining a fast and efficient website, ensuring a positive user experience, and keeping the site's content organized and accessible. Here, we'll explore best practices for handling media files, from upload to organization, optimization, and backup.
WordPress media files
As a WordPress user, you understand the importance of creating engaging and visually appealing content to captivate your audience. One crucial aspect of this endeavor is the effective management of media files, such as images, videos, and audio clips. These multimedia elements can greatly enhance the user experience and convey your message more effectively. However, failing to properly organize and optimize these files can lead to a cluttered and sluggish website, frustrating both you and your visitors.
Importance of managing media files in WordPress
Proper media file management is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures a smooth and efficient user experience by reducing page load times and preventing broken links or missing media. Secondly, it aids in maintaining a well-structured and organized website, making it easier for you to locate and update specific files when needed. Additionally, optimized media files can significantly improve your website's search engine rankings by enhancing its performance and accessibility.
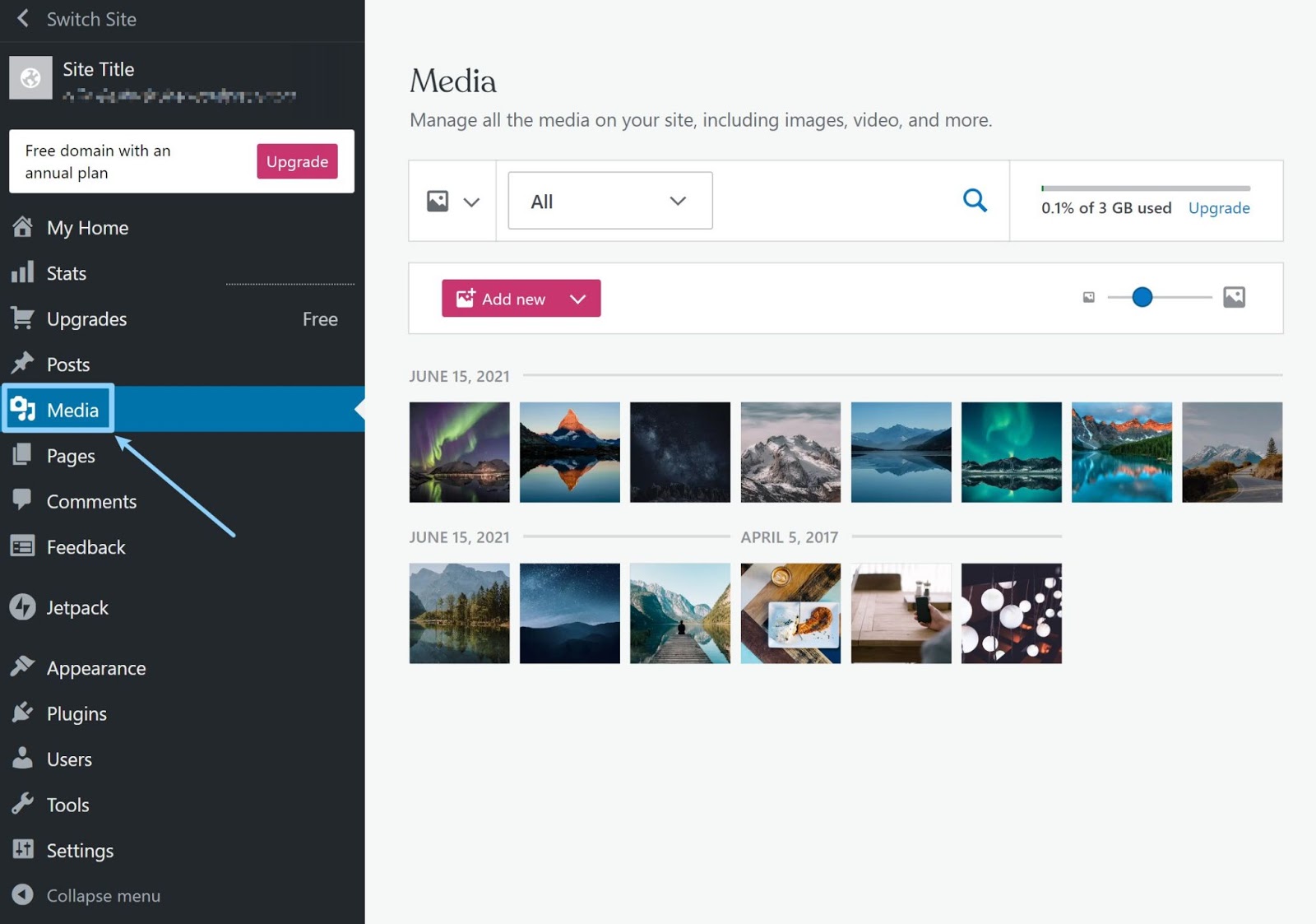
Best practices for organizing media files in WordPress
Establishing a clear and consistent file organization system is the foundation for effective media file management in WordPress. One approach is to create separate folders or categories based on content types, such as images, videos, or audio files. Within these categories, you can further subdivide files based on their purpose or associated blog posts or pages. This hierarchical structure not only keeps your media library organized but also simplifies the process of locating and managing specific files.
Additionally, consider implementing a naming convention that accurately describes the file's content and purpose. For example, using descriptive names like "blog-post-featured-image.jpg" or "product-video-tutorial.mp4" can make it easier to identify and locate files quickly.
File Organization
-
Use Descriptive File Names: Before uploading media to WordPress, rename files using descriptive, human-readable names. This practice not only helps in SEO but also facilitates easier searching and management within the media library.
-
Organize with Folders: Consider using plugins such as FileBird or WP Media Folder to create folders within your WordPress media library. This can help in organizing files by category, post type, or event, making them easier to locate and manage.
-
Regular Cleanup: Periodically review and clean up your media library to remove unused or redundant files, which can save storage space and reduce backup size.
Image Optimization
-
Resize Images Before Upload: Avoid using high-resolution images that are larger than needed. Resize images to the maximum dimensions they will be displayed on your website before uploading.
-
Compress Images: Use image compression tools or plugins like WP Smush, ShortPixel, or TinyPNG to reduce file size without significantly affecting quality. This reduces page load times and conserves bandwidth.
-
Choose the Right File Formats: Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images requiring transparency, and WebP for a good balance between quality and file size, when supported.
-
Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images, which means images are only loaded when they enter the viewport (visible part of the web page). This can significantly improve loading times for pages with a lot of images.
Media Library Management
-
Alt Text, Titles, and Descriptions: Always fill out the Alt Text for images, which aids in SEO and accessibility. Additionally, providing titles and descriptions can help with SEO and provide context when searching through the media library.
-
Consistent Usage of Thumbnails: Ensure your theme and plugins generate and use thumbnails appropriately. Thumbnails are smaller versions of your images that load faster, ideal for previews and gallery views.
Video and Audio Management
-
Host Large Files Externally: To save server resources and bandwidth, host large video and audio files on external platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, or SoundCloud, and embed them in your WordPress posts and pages.
-
Consider Accessibility: Provide subtitles and transcripts for videos and audio to enhance accessibility and SEO.
Security and Permissions
-
Set Correct File Permissions: Ensure that your media files are not writable by everyone. Typical permissions for files are 644, and for directories, 755. This prevents unauthorized modifications.
-
Secure Uploads: Utilize security plugins to scan and prevent malicious uploads and protect your media uploads directory.
Backup and Recovery
-
Regular Backups: Implement a solid backup strategy that includes your media files. Use plugins like UpdraftPlus or BackupBuddy to schedule automatic backups and store them off-site (e.g., Amazon S3, Dropbox).
-
Version Control: For critical media files, consider using version control systems or plugins that allow you to revert to previous versions of files.
Performance and Caching
-
CDN Services: Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve media files. CDNs can drastically reduce load times by serving files from servers close to the user's location.
-
Caching Static Resources: Configure caching for static resources such as images, JS, and CSS files. This can reduce server load and make pages load faster.
Accessibility
- Ensure Accessibility: Add meaningful Alt text for images, use captions where necessary, and choose color contrasts that comply with accessibility standards.
Responsive Images
-
Use Responsive Image Techniques: WordPress supports responsive images out of the box through the
srcsetattribute, which allows the browser to choose the most appropriate image size based on the device's screen size. Make sure your theme properly utilizes this feature to serve optimal image sizes. -
Test on Various Devices: Regularly check how media displays across different devices. This ensures that images, videos, and other media types are properly optimized for mobile, tablet, and desktop viewing, providing a good user experience across all platforms.
SEO for Media Files
-
Structured Data for Images and Videos: Enhance your SEO strategy by including structured data for media files. Use schema markup to provide search engines with specific information about your media content, such as images in articles, video objects, or galleries.
-
Integrate Media into Your XML Sitemaps: Ensure that your media files are included in your XML sitemaps. This makes it easier for search engines to find and index them, which can enhance the visibility of your content in image and video search results.
Accessibility Compliance
-
Audit Media for Accessibility: Regularly audit your website’s media content for accessibility compliance. Use tools that can help identify images missing alt text, videos lacking captions, and audio files missing transcripts. This ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can access and benefit from your content.
-
Accessible Media Players: If you host video or audio content directly on your WordPress site, use media players that are compliant with accessibility standards. These players should support keyboard navigation and be compatible with screen readers.
Integration with Media Libraries
-
Cloud Storage Integration: To save server space and potentially increase load times, integrate your WordPress site with external media libraries like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure. These services can host your media files and serve them directly to your users.
-
Automated Media Optimization Tools: Leverage tools that automatically optimize media files as they are uploaded. Plugins like EWWW Image Optimizer or Imagify can automatically adjust compression levels, resize images, and convert images to more efficient formats.
Monitoring and Analytics
-
Use Analytics to Track Media Performance: Implement tracking on your media files to see which images or videos perform best. This can help inform your content strategy by understanding what type of media engages your audience the most.
-
Monitor Load Times: Regularly monitor the impact of media on your site’s load time. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest can provide insights into how media affects performance and offer suggestions for improvement.
Legal Considerations
-
Copyrights and Licensing: Always ensure you have the right to use a media file before uploading it to your site. Respect copyright laws and obtain necessary permissions or licenses. When in doubt, opt for royalty-free or Creative Commons-licensed media.
-
Proper Attribution: Where required, make sure to give proper attribution to media creators according to the licensing agreements. This not only respects the creator's rights but also adds credibility to your site.
Training and Documentation
-
Educate Your Team: If you work with a team, make sure everyone understands these best practices for managing media files. Provide training sessions or documentation to help them follow these guidelines.
-
Document Your Media Handling Procedures: Create a reference document that outlines your procedures for uploading, optimizing, and managing media. This ensures consistency, especially as your team grows or changes.

Understanding file formats and optimizing media files for web
Not all media file formats are created equal when it comes to web performance. Certain formats, such as JPEG for images and MP4 for videos, are generally more optimized for the web and offer better compression and loading times. However, it's essential to strike a balance between file size and quality to ensure a visually appealing experience without compromising performance.
To optimize your media files, consider using image compression tools or plugins that can reduce file sizes without significantly compromising quality. For videos, you may need to transcode them to a web-friendly format and adjust settings like bitrate and resolution to achieve the desired balance between quality and file size.
Using plugins and tools to manage media files in WordPress
WordPress offers a range of plugins and tools to streamline the process of managing media files. For example, plugins like Enhanced Media Library or Media File Renamer can help you organize, rename, and categorize your files more efficiently. Other plugins, such as Smush or Imagify, are specifically designed for image optimization, automatically compressing and resizing your images to improve page load times.
Additionally, consider using a content delivery network (CDN) to serve your media files from multiple locations around the world, reducing latency and improving load times for visitors from different geographical regions.
Properly naming and labeling media files for better organization
Implementing a consistent and descriptive naming convention for your media files is crucial for maintaining an organized and easily navigable media library. When naming files, consider including relevant information such as the file type, content subject, and date or version number. For example, "blog-post-featured-image-20230501.jpg" or "product-video-tutorial-v2.mp4" can provide valuable context and make it easier to locate and manage specific files.
Additionally, take advantage of the built-in labeling and categorization features in WordPress to further organize your media files. You can assign tags, categories, or custom taxonomies to your files, making it easier to filter and search for specific types of media across your website.
Managing file sizes and compression for faster loading times
Large media files, particularly high-resolution images and videos, can significantly impact your website's performance and loading times. To mitigate this issue, it's essential to optimize your media files by reducing their file sizes through compression techniques.
For images, consider using lossless compression methods like PNG or WebP formats, which can significantly reduce file sizes without compromising visual quality. Additionally, you can leverage WordPress plugins like Smush or Imagify to automatically optimize your images upon upload.
For videos, transcoding them to web-friendly formats like MP4 or WebM can help reduce file sizes while maintaining acceptable quality. Additionally, adjusting settings like bitrate, resolution, and frame rate can further optimize video files for faster streaming and loading times.
Implementing a backup system for WordPress media files
While managing and optimizing your media files is crucial, it's equally important to implement a robust backup system to safeguard against data loss or corruption. WordPress offers built-in backup and export features, allowing you to create complete backups of your entire website, including media files.
However, for larger media libraries or more comprehensive backup solutions, consider using dedicated backup plugins or services specifically designed for WordPress. These tools often provide automated backup scheduling, off-site storage options, and easy restoration capabilities, ensuring that your valuable media files are protected and can be quickly recovered in case of any mishaps.
Integrating media files with your content and optimizing for SEO
Effectively integrating media files into your content can not only enhance the user experience but also contribute to better search engine optimization (SEO). When adding images or videos to your WordPress posts or pages, be sure to include relevant alt text and descriptions to improve accessibility and provide context for search engines.
Additionally, consider optimizing your media file names and metadata with relevant keywords to improve their visibility and ranking in search engine results. For example, using descriptive file names like "keyword-optimized-blog-post-image.jpg" can help search engines better understand the content and context of your media files.
Frequently Asked Questions About WordPress Media Management

Use descriptive file names for better searchability and SEO. Consider using media library management plugins like FileBird or WP Media Folder to create folders and categorize files by type, topic, or date, which can help maintain an organized library.
Resize images to the maximum display size needed before uploading them. Compress images using tools or plugins like WP Smush, ShortPixel, or TinyPNG. Also, ensure that your website uses appropriate formats (JPEG, PNG, WebP) and consider implementing lazy loading for images.
Regularly back up your media files using plugins like UpdraftPlus or BackupBuddy. Store backups in a secure, off-site location like Amazon S3 or Dropbox to protect against data loss. Ensure that both your database and your media files are included in the backups.
Yes, host large video and audio files on external platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, or SoundCloud and embed them in your site. For images, use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to distribute the load and decrease site latency.
Add alt text to images for screen readers and SEO benefits. Provide captions and transcripts for videos and audio files. Use accessible media players that support keyboard navigation and are screen reader friendly.
Set proper file permissions (typically 644 for files and 755 for directories). Use security plugins to monitor and protect uploads, and consider implementing solutions that prevent the execution of PHP within the uploads directory.
Utilize alt text and title tags effectively. Include structured data for media where appropriate. Ensure that media files are included in your XML sitemaps, and consider adding image-specific metadata to enhance visibility in search results.
Yes, several plugins can automate image optimization. Plugins like EWWW Image Optimizer, Imagify, or Autoptimize can automatically compress images upon upload and also offer bulk optimization options for existing files.
Only upload media that you own or have permission to use. Utilize stock photography sites with proper licensing or Creative Commons for free-to-use options. Always provide attribution as required by the license and document your rights to use the media.
Use performance monitoring tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to understand how media affects your site's load time and overall performance. These tools can offer insights and suggestions for optimization.
Conclusion: Streamlining your WordPress media file management process
Effective media file management is crucial for maintaining a well-organized, visually appealing, and high-performing WordPress website. By implementing best practices such as consistent file organization, optimized file formats, and proper naming conventions, you can streamline your workflow and enhance the overall user experience.
Additionally, leveraging plugins and tools specifically designed for media file management can automate many tasks and simplify the process. Remember to prioritize regular backups to safeguard your valuable media assets and ensure seamless integration of media files with your content for better search engine optimization.
By following these best practices, you can take control of your WordPress media library, ensuring a clutter-free and efficient website that delivers an exceptional experience to your visitors.
Are you struggling to manage your WordPress media files effectively? Don't let disorganized and unoptimized media assets hold back your website's performance and user experience. Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive WordPress media file management solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our team of experts will work closely with you to implement best practices, optimize your media files, and streamline your workflow, ensuring a seamless and engaging experience for your visitors.





