How to set up subdomains in DNS settings?
Navigating through the technical landscape of DNS settings and subdomains can initially appear daunting. However, with a structured approach and clear guidance, you'll find that setting up subdomains is a manageable and even rewarding task. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, ensuring you have all the knowledge and tools at your disposal to successfully configure subdomains in your DNS settings.
Creating subdomains is a fundamental aspect of managing a domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) settings. Subdomains are extensions of your main domain that can direct users to different sections of your website or to entirely different services. For example, blog.example.com and shop.example.com are subdomains of example.com. Setting up subdomains involves configuring DNS records to ensure that each subdomain correctly points to its designated target, whether it’s a specific IP address or another domain.
Understanding Subdomains and DNS Settings
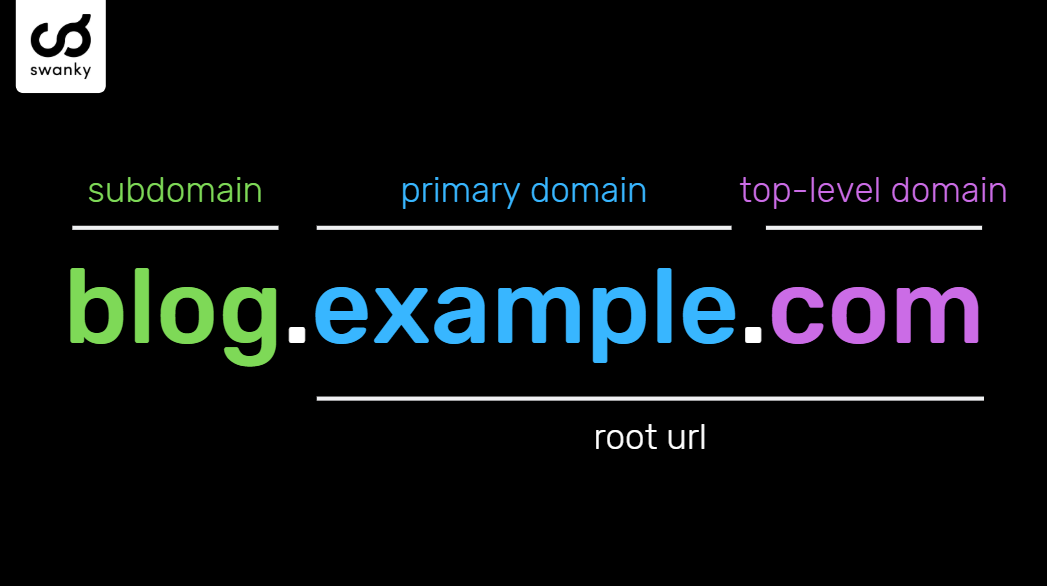
Before diving into the intricacies of configuring subdomains, it's crucial to grasp what subdomains and DNS settings actually are. Subdomains serve as extensions of your primary domain, offering a way to organize and navigate different sections of your website efficiently. For instance, you might encounter a subdomain like blog.example.com, where "blog" is the subdomain, "example" is the primary domain, and ".com" is the top-level domain (TLD).
DNS, which stands for Domain Name System, is the internet's equivalent to a phone book. It translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network. DNS settings are configurations made to DNS records, guiding how traffic is directed on the internet. Understanding these concepts is the first step in mastering the configuration of subdomains.
Subdomains not only enhance the organizational structure of a website but also play a significant role in optimizing its SEO and improving user experience. They make it possible to assign different sections of a site a unique identity, without the need to purchase additional domain names.
Why Configure Subdomains in DNS Settings?
The decision to configure subdomains within DNS settings comes with a multitude of benefits. Primarily, it allows for the segregation of website content, making it easier for visitors to find what they are looking for. For businesses, this can mean separating a blog section from the main e-commerce site, or for educational institutions, offering a distinct area for students and faculty.
Moreover, subdomains can significantly boost SEO efforts. Search engines like Google treat subdomains almost as separate entities, which means you can target specific keywords or audience segments more effectively. This segmentation can lead to improved search engine rankings and, consequently, increased traffic.
Configuring subdomains also enhances the scalability of your web presence. As your business or project grows, you can add more subdomains to cater to new services, products, or information sectors without the need to overhaul your primary website. This flexibility is invaluable in the fast-paced digital world.
Types of Subdomains
Subdomains come in various forms, each serving different purposes. The most common type is the "service" subdomain, such as "shop.example.com," where the subdomain directs users to a specific service provided by the website. "Location" subdomains, like "uk.example.com," cater to geographical targeting, presenting content relevant to users in specific regions. "Community" subdomains, such as "forum.example.com," create dedicated spaces for user interaction and engagement.
Understanding the different types of subdomains available helps in planning the architecture of your website more effectively. It allows you to tailor your approach to suit your specific needs and objectives, ensuring that your subdomains add value to your overall web presence.
Access Your DNS Management Interface
To begin configuring subdomains, you first need to access your DNS settings. This process varies depending on your hosting provider but generally involves logging into your web hosting account and navigating to the domain management section. Look for a link or tab that says "DNS Settings," "Domain Settings," or something similar.
Once you've located your DNS settings, take a moment to familiarize yourself with the interface. You'll likely see a list of DNS records, including A records, CNAME records, MX records, and more. Understanding the purpose of each record type is key to configuring your subdomains correctly.
Should you encounter any difficulties accessing your DNS settings, don't hesitate to reach out to your hosting provider's support team. They can provide guidance and ensure you're looking in the right place.
To begin, you need to access the DNS management panel where your domain’s DNS settings are controlled. This is typically provided by your domain registrar (such as GoDaddy, Namecheap, etc.), though your DNS might be managed by your hosting provider if you’ve delegated control to them.
- Log into your account where your domain is registered.
- Navigate to the DNS Management page. This can usually be found in the domain settings or similar section.
Decide on the Subdomain Name
Before you proceed with the DNS settings, you should decide on the name of your subdomain. Subdomains should be concise and clearly related to their function, like store, blog, mail, or support.
Creating a New Subdomain
With your DNS settings open, the next step is to create a new subdomain. This is usually done by finding an option labeled "Add Subdomain," "Create New Subdomain," or something along those lines. Clicking on this option will prompt you to enter the name of your subdomain.
When choosing a name for your subdomain, keep it short, memorable, and relevant to the content or service it will host. After typing in your subdomain name, you'll also select the domain to which it will be attached. Confirm your choices, and the new subdomain will be created.
It's worth noting that it may take some time for the new subdomain to propagate across the internet. This is a normal part of the process, so don't be alarmed if your subdomain isn't immediately accessible.
Configuring DNS Records for the Subdomain
Configuring DNS records for your new subdomain is where the technical aspects come into play. The most common record types you'll deal with are A records and CNAME records. An A record points a domain or subdomain to an IP address, while a CNAME record points a domain or subdomain to another domain name.
For most subdomain configurations, you'll be using an A record. You'll need to know the IP address of the server hosting your subdomain's content. Once you have this information, create a new A record for your subdomain, entering the subdomain name and the corresponding IP address.
If your subdomain's content is hosted on a platform that prefers using CNAME records (like some CDN or SaaS platforms), create a CNAME record instead. Enter your subdomain name and the platform's domain name as directed by the platform's setup instructions.
Create DNS Records for Your Subdomain
In the DNS management interface, you will create DNS records. The most common types used for subdomains are A, CNAME, and sometimes MX records.
- A Record: This points a domain or subdomain to an IP address.
- CNAME Record: This points a domain or subdomain to another domain name, not an IP.
A Record Setup
- Find the option to Add Record or similar.
- Select or enter
Aas the type of record. - In the Host field, enter the subdomain part only (e.g., for
blog.example.com, just enterblog). - In the Value or Points to field, enter the IP address where the subdomain content is hosted.
- Save or Add Record.
CNAME Record Setup
- Choose to Add Record.
- Select
CNAMEas the type of record. - In the Host field, enter the subdomain part (e.g.,
shopforshop.example.com). - In the Value or Points to field, enter the target domain (e.g.,
user.github.iofor a GitHub Pages site). - Save or Add Record.
Verify the DNS Records
After setting up DNS records for your subdomain, it is important to verify that they are working properly.
- Use a tool like
digornslookupto check your DNS settings. For example,nslookup blog.example.com. - Verify that the response shows the correct IP address or CNAME target as you configured.
Wait for DNS Propagation
DNS changes can take anywhere from a few minutes to 48 hours to propagate worldwide. During this time, the new subdomain may not be immediately accessible to everyone.
Test the Subdomain
Once DNS propagation is complete, test the subdomain by navigating to it in a web browser. It should load the intended content hosted on the specified server or service.
After configuring the DNS records for your subdomain, it's crucial to test that everything is working correctly. This can be done using online tools that check DNS records and propagation. Enter your subdomain, and the tool will tell you if it's correctly pointing to the intended IP address or domain name.
Additionally, try accessing your subdomain in a web browser. If the configuration is correct, you should see the content you've set up for this subdomain. Remember, DNS changes can take up to 48 hours to fully propagate, so if it doesn't work immediately, give it some time.
Consider Additional Configuration
Depending on your needs, you may want to configure other settings for your subdomain, such as:
- SSL/TLS certificates: To secure your subdomain, particularly if it's used for e-commerce or any form of user registration.
- Email settings (MX records): If you're setting up a mail subdomain, you'll need to configure MX records to handle email delivery properly.
Best Practices for Subdomain Configuration
When configuring subdomains, adhering to best practices can prevent issues and optimize performance. Always use clear and descriptive names for your subdomains, which reflect their purpose. Regularly review your DNS settings to ensure that all records are up-to-date and correct.
Security is also a critical consideration. Implement HTTPS by securing your subdomains with SSL certificates, protecting your users' data and boosting your site's credibility. Additionally, monitor your subdomains for any unusual activity, as they can be targets for cyber threats just like your main domain.
Advanced Tips and Best Practices for Managing Subdomains
After you have your basic subdomain setup completed, there are a few advanced tips and best practices that can help optimize your subdomain management and enhance the performance and security of your website.
Optimize DNS Records
Managing DNS effectively is crucial for the performance and reliability of your subdomains. Here are a few tips:
- Use TTL (Time to Live) wisely: TTL dictates how long DNS servers cache the information of your DNS records. Setting a shorter TTL can be beneficial during changes as it means the cache is updated more frequently. However, longer TTLs can reduce the DNS lookup time and reduce the load on your DNS servers.
- Consider using ANAME records: If your DNS host supports it, ANAME records can be a powerful tool. They function like A records but can point to a hostname like CNAME records. This is particularly useful when you need to point a root domain to a hostname, which CNAME records cannot do.
Security Considerations
Securing your subdomains is just as important as securing your main domain. Here are essential security measures:
- SSL/TLS certificates for each subdomain: Ensure every subdomain has a valid SSL/TLS certificate to secure data transfer. This is crucial if you're collecting sensitive information or engaging in e-commerce. Many services like Let’s Encrypt offer free certificates which can be automated with tools like Certbot.
- Subdomain isolation: If possible, host different services on different subdomains in isolated environments. This reduces the risk that a security breach in one part of your site could compromise the entire domain.
Subdomain and SEO
Subdomains can affect SEO, and how they're used can influence your website's search engine ranking.
- Consistent content themes: Search engines often treat subdomains almost like separate websites. Ensure that each subdomain has a consistent theme or category of content to help search engines better understand and rank your site.
- Cross-linking: Intelligently link between your subdomains and main domain to boost SEO. This can help spread domain authority across your entire web presence.
- Canonical tags: Use canonical tags if you have similar content across subdomains and the main domain. This helps prevent issues of content duplication in search engine indexes.
Monitoring and Analytics
To ensure your subdomains are performing well and to gain insights into user behavior:
- Use separate analytics tracking: Consider using separate analytics tracking for each subdomain. This approach allows you to better understand the traffic and behavior specific to each subdomain. Google Analytics and other tools can be configured to track subdomains separately or together as you prefer.
- Regular audits: Periodically review the performance and security of your subdomains. Look for areas to improve and keep an eye on emerging security threats.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering issues when configuring subdomains is not uncommon. If your subdomain isn't working as expected, there are a few common areas to check. First, verify that the DNS records are correctly entered and that there are no typos. Next, ensure that the server or platform hosting your subdomain's content is properly configured to accept requests for your subdomain.
Sometimes, the issue may be related to DNS propagation delays. If you've recently made changes, wait at least 48 hours to see if the issue resolves on its own. If problems persist, consulting your hosting provider's support team can provide additional insights and assistance.
Setting up subdomains can sometimes lead to issues. Here are common troubleshooting tips:
- Propagation delay: If your subdomain isn't accessible immediately, it might be due to DNS propagation delays. Use online tools to check the global DNS propagation status for your subdomain.
- Misconfigured records: Double-check your DNS records. A common mistake is entering the full URL in the DNS settings when only the subdomain prefix is required.
- Server configuration: Ensure that the server hosting the subdomain content is configured to respond to the subdomain requests. This often involves adjusting server settings or virtual host configurations.
FAQ: Setting Up and Managing Subdomains

A subdomain is a prefix added to your main domain name, creating a secondary, distinct web address that can be used to host additional content, services, or features related to your main website. For example, blog.example.com is a subdomain of example.com.
Subdomains can help organize your website into distinct sections, each potentially serving different purposes (like a store, blog, or support center). They can also be useful for SEO purposes, managing large sites, or hosting separate applications without needing new domain names.
DNS changes can take anywhere from a few minutes up to 48 hours to fully propagate worldwide. The exact time depends on the TTL (Time to Live) value set for your DNS records.
Yes, you should secure each subdomain with an SSL/TLS certificate to ensure encrypted connections. Certificates can be applied to each subdomain specifically or included under a wildcard certificate that covers all subdomains of a domain.
Subdomains can impact SEO as search engines may treat them as separate entities from the main domain. It's important to maintain consistent, high-quality content on each subdomain and use proper SEO strategies, such as cross-linking and correct use of canonical tags to optimize performance.
- Log into your DNS provider’s control panel.
- Decide on the subdomain name.
- Create an A record or CNAME record for the subdomain pointing to the appropriate IP address or hostname.
- Verify the DNS settings using tools like
nslookupordig. - Wait for DNS propagation to complete.
- Test the subdomain by accessing it in a web browser.
Yes, a subdomain can be directed to an external website by setting up a CNAME record that points to the external website’s domain name.
The number of subdomains you can create is typically not limited by DNS providers, but keep in mind that managing a large number of subdomains can become complex. Some hosting providers might have limits, so it's good to check with them.
A subdomain (e.g., blog.example.com) serves content from a separate section or domain, potentially on different servers. A subdirectory (e.g., example.com/blog) is a part of the main website and hosted on the same server, serving as just another folder within the main domain.
- Check if DNS records are correctly set and propagated.
- Ensure server configurations accept requests for the subdomain.
- Verify that there is no typo in the DNS records.
- Use diagnostic tools like
pingortracerouteto check network connectivity.
Conclusion
Configuring subdomains in your DNS settings is a powerful way to enhance your website's structure, improve user experience, and optimize for search engines. By following the step-by-step guide provided, from understanding subdomains and DNS settings to troubleshooting common issues, you're well-equipped to tackle this task with confidence.
Remember, patience and attention to detail are key. DNS changes can take time to propagate, and meticulous configuration ensures your subdomains function as intended. With practice and adherence to best practices, you'll find that managing subdomains becomes a straightforward part of your web management repertoire. If you need more information or support about subdomain DNS management Let's connect!





