
How to secure DNS against attacks?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical component of the internet infrastructure, functioning as the phonebook of the digital world. It translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing you to access websites and services without memorizing complex numerical sequences. However, this vital role also makes DNS a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities and launch attacks.
As a cornerstone of internet communication, DNS security is paramount for maintaining the integrity and availability of online services. When DNS is compromised, the consequences can be severe, ranging from website downtime to data breaches and financial losses. Understanding the importance of DNS in cybersecurity is the first step toward implementing robust protection measures.
To grasp the significance of DNS security, consider the following analogy: imagine DNS as the navigation system of the internet. Just as a faulty GPS can lead you astray, a compromised DNS can misdirect users to malicious websites or prevent them from reaching their intended destinations. By securing your DNS infrastructure, you're essentially safeguarding the roadmap of your digital presence.
Common DNS Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
DNS faces a variety of security threats that can compromise its functionality and put your organization at risk. Some of the most prevalent DNS security challenges include:
-
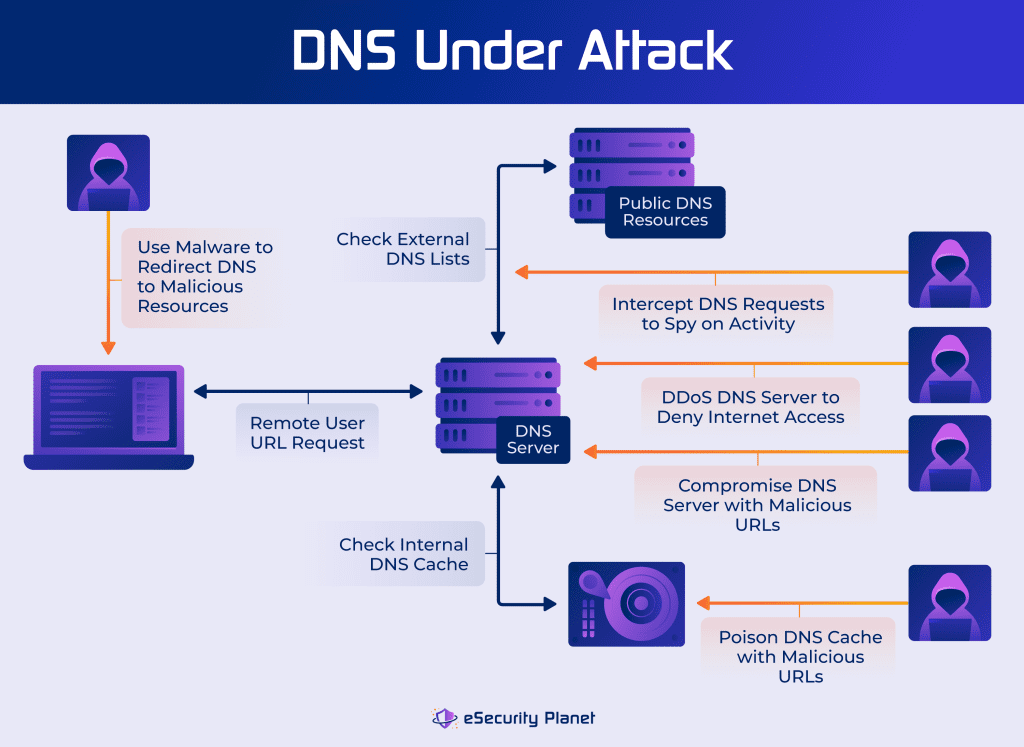
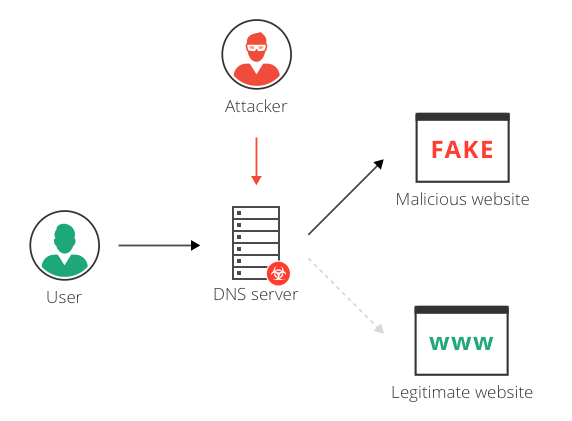
DNS Spoofing/Cache Poisoning Attackers insert malicious data into a DNS resolver's cache, redirecting users to fraudulent websites.
-
DNS Amplification Attacks These are a form of Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks where attackers use open DNS resolvers to flood a target with amplified traffic.
-
Domain Hijacking Cybercriminals gain control of a domain's DNS settings, potentially redirecting traffic or taking websites offline.
-
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks Attackers intercept DNS queries to alter or eavesdrop on communication.
-
DNS Tunneling Malicious actors use DNS to exfiltrate data or communicate with command-and-control servers.
-
DNS Typosquatting Attackers register domain names similar to legitimate ones, tricking users into visiting malicious sites.
-
Zone Transfer Attacks Unauthorized users attempt to copy entire DNS zones, potentially exposing sensitive information.s.
These threats exploit various vulnerabilities in DNS architecture, such as:
- Insufficient authentication mechanisms
- Lack of encryption in DNS queries
- Misconfigured DNS servers
- Outdated DNS software with known security flaws
Understanding these threats and vulnerabilities is crucial for developing a comprehensive DNS security strategy tailored to your organization's needs.
The Consequences of DNS Attacks on Businesses
The impact of DNS attacks on businesses can be far-reaching and devastating. When your DNS infrastructure is compromised, the repercussions extend beyond mere technical inconveniences, affecting your organization's operations, reputation, and bottom line.
One of the most immediate consequences is service disruption. A successful DNS attack can render your website and online services inaccessible, leading to lost revenue and frustrated customers. For e-commerce platforms, even a few minutes of downtime can translate to significant financial losses.
Data breaches are another serious outcome of DNS attacks. By redirecting users to malicious sites, attackers can harvest sensitive information, including login credentials and financial data. This not only puts your customers at risk but also exposes your organization to legal liabilities and regulatory penalties.
The long-term damage to your brand reputation can be equally severe. Once trust is broken, rebuilding customer confidence becomes an uphill battle. Negative publicity surrounding a DNS attack can deter potential clients and partners, impacting your business growth for years to come.
Essential DNS Security Best Practices
Implementing robust DNS security measures is crucial for protecting your organization against potential threats. Here are some essential best practices to enhance your DNS security posture:
Use DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions)
DNSSEC adds an additional layer of security by digitally signing DNS data. This ensures that responses come from the correct source and haven't been tampered with.
- How to Implement:
- Enable DNSSEC for your domain via your domain registrar.
- Regularly monitor and maintain DNSSEC records to ensure their integrity.
Enable DNS Filtering
DNS filtering blocks access to known malicious domains, preventing users from inadvertently visiting harmful sites.
- Steps:
- Use a reputable DNS filtering service.
- Configure network devices to route DNS queries through the filtering service.
Limit Recursive DNS Queries
Restricting recursive queries prevents unauthorized users from exploiting your DNS server.
- Implementation Tips:
- Configure DNS servers to only handle queries from trusted sources.
- Use Access Control Lists (ACLs) to define permitted IP ranges.
Monitor and Log DNS Activity
Monitoring DNS traffic helps you detect anomalies, such as unusual query patterns or unauthorized changes.
- Tools and Strategies:
- Deploy DNS monitoring tools like Splunk or Zabbix.
- Regularly review DNS logs for suspicious activity.
Implement Rate Limiting
Rate limiting reduces the impact of DNS amplification and other volumetric attacks.
- Steps:
- Configure your DNS server to limit the number of queries it processes from a single source.
- Use tools like iptables or server-specific rate-limiting features.
Secure Zone Transfers
Zone transfers, if unsecured, can expose sensitive DNS data to attackers.
- Best Practices:
- Restrict zone transfers to specific IP addresses.
- Use secure transfer methods like TSIG (Transaction Signatures).
Keep DNS Software Updated
Outdated DNS software can have vulnerabilities that attackers exploit.
- Recommendations:
- Regularly update DNS software, including BIND, Unbound, or other DNS servers.
- Subscribe to vendor security alerts for timely updates.
Use DNS Encryption
Encrypting DNS queries enhances privacy and security by preventing eavesdropping and MITM attacks.
- Options:
- Implement DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) or DNS-over-TLS (DoT).
- Ensure client devices and DNS servers support these protocols.
Deploy Redundant DNS Servers
Redundancy ensures continued availability even if one server is compromised or offline.
- Action Plan:
- Set up multiple geographically distributed DNS servers.
- Use anycast routing to direct queries to the nearest server.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Periodic audits help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in your DNS infrastructure.
- Checklist:
- Review DNS configurations for misconfigurations.
- Test for susceptibility to common attacks using penetration testing tools.
These best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of DNS-related security incidents and build a more resilient infrastructure.
Implementing DNSSEC: A Crucial Step in DNS Protection
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is a set of protocols designed to add an extra layer of security to the DNS infrastructure. Implementing DNSSEC is a critical step in protecting your domain against various DNS-based attacks, particularly cache poisoning and DNS spoofing.
DNSSEC works by digitally signing DNS records, allowing resolvers to verify the authenticity and integrity of DNS responses. This cryptographic validation ensures that the information received from DNS servers is legitimate and has not been tampered with during transmission.
To implement DNSSEC effectively:
- Generate DNSSEC keys for your domain
- Sign your DNS zone with these keys
- Publish the signed records and the corresponding public keys
- Configure your DNS servers to support DNSSEC
- Coordinate with your domain registrar to establish a chain of trust
While DNSSEC implementation can be complex, the benefits far outweigh the challenges. It provides a robust defense against many DNS-based attacks and enhances the overall trustworthiness of your online presence.
DNS Filtering and Monitoring for Enhanced Security
DNS filtering and monitoring are powerful tools in your arsenal against DNS-based threats. By implementing these measures, you can proactively identify and block malicious activities before they can cause harm to your network.
DNS filtering works by screening DNS queries against a database of known malicious domains and IP addresses. When a user attempts to access a flagged site, the DNS filter blocks the connection, preventing potential infections or data exfiltration. This approach is particularly effective in combating phishing attacks and malware distribution.
Key benefits of DNS filtering include:
- Protection against newly registered malicious domains
- Customizable filtering policies based on your organization's needs
- Reduced strain on network resources by blocking threats at the DNS level
DNS monitoring, on the other hand, involves continuous analysis of DNS traffic patterns to detect anomalies that may indicate an ongoing attack. Advanced monitoring solutions use machine learning algorithms to establish baseline behavior and flag suspicious activities in real-time.
Implementing both DNS filtering and monitoring creates a robust defense mechanism, allowing you to:
- Identify potential DNS-based attacks early
- Block access to malicious websites and command-and-control servers
- Gain visibility into your network's DNS traffic patterns
- Respond quickly to emerging threats
The Role of DNS Firewalls in Threat Prevention
DNS firewalls play a crucial role in bolstering your organization's security posture by providing an additional layer of protection against DNS-based threats. Unlike traditional firewalls that focus on IP addresses and ports, DNS firewalls specifically target the domain name resolution process.
These specialized firewalls work by intercepting DNS queries and comparing them against regularly updated threat intelligence feeds. When a query matches a known malicious domain, the DNS firewall can take various actions, such as:
- Blocking the query outright
- Redirecting the user to a safe landing page
- Logging the attempt for further investigation
- The benefits of implementing a DNS firewall include:
Proactive Threat Prevention: By blocking malicious domains before a connection is established, DNS firewalls prevent threats from entering your network.
Reduced False Positives: DNS firewalls typically have lower false-positive rates compared to traditional security solutions.
Enhanced Visibility: These firewalls provide valuable insights into DNS traffic patterns and potential security incidents.
Compliance Support: Many DNS firewall solutions offer features that help meet regulatory requirements for data protection and cybersecurity. To maximize the effectiveness of your DNS firewall:
- Regularly update threat intelligence feeds
- Customize filtering rules based on your organization's specific needs
- Integrate the DNS firewall with your existing security infrastructure
- Monitor and analyze firewall logs for continuous improvement
Securing DNS in Cloud Environments
As organizations increasingly migrate their infrastructure to the cloud, securing DNS in these environments becomes paramount. Cloud-based DNS services offer scalability and flexibility, but they also introduce unique security challenges that require careful consideration.
When securing DNS in cloud environments, consider the following strategies:
Use Cloud-Native Security Features: Leverage the security features provided by your cloud service provider, such as access controls and encryption options for DNS services.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Require strong authentication methods for accessing and managing DNS settings in your cloud environment.
Utilize Private DNS Zones: Where possible, use private DNS zones to restrict access to internal resources and minimize exposure to the public internet.
Enable Logging and Monitoring: Take advantage of cloud-native logging and monitoring tools to track DNS activities and detect anomalies.
Regularly Review DNS Configurations: Conduct periodic audits of your cloud DNS settings to ensure they align with your security policies.
Implement DNS-Based Security Services: Utilize cloud-based DNS security services that offer features like threat intelligence integration and DNS filtering.
Ensure Proper IAM Configurations: Implement robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to control who can make changes to DNS settings.
Adopting these practices, you can create a secure DNS infrastructure in your cloud environment, mitigating risks associated with DNS-based attacks and misconfigurations.
DNS Security Tools and Solutions
A wide array of DNS security tools and solutions are available to help you protect your DNS infrastructure. These tools range from open-source utilities to enterprise-grade security platforms. Here's an overview of some essential DNS security tools:
DNS Auditing Tools:
- DNSInspect: Analyzes DNS configurations for misconfigurations and security issues.
- DNSViz: Provides visual analysis of the DNSSEC authentication chain.
DNS Monitoring Solutions:
- BIND9: Offers built-in DNS query logging and analysis capabilities.
- DNSWatch: Provides real-time DNS traffic monitoring and threat detection.
DNS Firewall Solutions:
- Infoblox DNS Firewall: Offers comprehensive DNS protection with threat intelligence integration.
- BlueCat DNS Edge: Provides DNS security at the network edge with advanced analytics.
DNSSEC Tools:
- OpenDNSSEC: Automates the process of DNSSEC signing and key management.
- BIND DNSSEC Tools: A suite of utilities for managing DNSSEC keys and signatures.
DNS Encryption Tools:
- DNSCrypt: Encrypts DNS traffic between the client and resolver.
- Stubby: A DNS Privacy stub resolver supporting DNS-over-TLS.
When selecting DNS security tools, consider factors such as:
- Compatibility with your existing infrastructure
- Ease of integration and management
- Scalability to meet your organization's growth
- Frequency of updates and threat intelligence feeds
- Support for emerging DNS security standards
Implementing a combination of these tools can significantly enhance your DNS security posture and provide comprehensive protection against various threats.
Future Trends in DNS Security: AI and Machine Learning
The landscape of DNS security is continuously evolving, with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) emerging as game-changing technologies in the fight against DNS-based threats. These advanced technologies are poised to revolutionize how organizations detect, prevent, and respond to DNS security incidents.
Some key areas where AI and ML are making an impact in DNS security include:
Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of DNS traffic data to establish baseline behavior and identify unusual patterns that may indicate an attack.
Predictive Threat Intelligence: Machine learning models can predict emerging DNS-based threats by analyzing historical data and identifying trends in attack vectors.
Automated Response: AI-powered systems can automatically respond to detected threats, such as updating DNS firewall rules or isolating compromised systems.
DNS Traffic Classification: ML algorithms can categorize DNS traffic with high accuracy, helping to identify malicious queries and potential data exfiltration attempts.
Zero-Day Threat Detection: AI can potentially identify previously unknown DNS-based threats by recognizing subtle indicators of malicious activity.
As these technologies mature, we can expect to see:
- More sophisticated DNS security solutions that leverage AI and ML capabilities
- Improved accuracy in threat detection with fewer false positives
- Faster response times to DNS-based attacks
- Enhanced ability to detect and mitigate complex, multi-vector attacks
To stay ahead of the curve, consider:
- Exploring DNS security solutions that incorporate AI and ML technologies
- Investing in training for your security team to effectively leverage these advanced tools
- Participating in industry forums and research initiatives focused on AI/ML in DNS security
Embracing these future trends, you can position your organization to tackle the evolving DNS threat landscape more effectively.
Training Your Team on DNS Security Protocols
Effective DNS security isn't just about implementing the right tools and technologies; it's also crucial to ensure that your team is well-versed in DNS security protocols and best practices. A well-trained team can be your first line of defense against DNS-based threats and can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to security incidents.
Here are some key areas to focus on when training your team:
DNS Fundamentals: Ensure that all team members have a solid understanding of how DNS works and its role in network infrastructure.
Common DNS Threats: Educate your team about various DNS-based attacks, their potential impact, and how to recognize signs of an ongoing attack.
Security Best Practices: Train staff on DNS security best practices, including proper configuration, regular auditing, and secure management of DNS records.
Incident Response: Develop and practice DNS-specific incident response procedures to ensure quick and effective action in case of a security breach.
DNSSEC Implementation: Provide in-depth training on DNSSEC, including key management, zone signing, and troubleshooting.
DNS Monitoring and Analysis: Teach your team how to effectively use DNS monitoring tools and interpret DNS traffic patterns.
Emerging Technologies: Keep your team updated on new DNS security technologies and trends, including AI and ML applications in DNS security.
Consider implementing the following training approaches:
- Regular workshops and seminars on DNS security topics
- Hands-on labs for practical experience with DNS security tools
- Simulated DNS attack scenarios for incident response practice
- Certification programs in DNS security and management
- Participation in DNS security conferences and webinars
Investing in comprehensive DNS security training for your team, you'll create a more resilient and responsive security posture, better equipped to handle the complex challenges of DNS protection.
FAQs About Securing DNS
DNSSEC secures DNS data by verifying its authenticity, preventing spoofing and MITM attacks.
DNS filtering blocks access to malicious domains, protecting users from phishing and malware.
Open recursive queries can be exploited for DDoS amplification attacks.
Update DNS software as soon as security patches are released to mitigate vulnerabilities.
DNS tunneling uses DNS queries to bypass firewalls and exfiltrate data or communicate with malicious servers.
Encryption enhances privacy and security but should be combined with other measures like DNSSEC and monitoring.
Monitoring detects suspicious activity, allowing you to respond to threats proactively.
Redundant servers ensure DNS availability during attacks or server failures.
Restrict transfers to trusted IPs and use TSIG for authentication.
Tools like DNSViz, Zabbix, and security scanners can identify vulnerabilities in your DNS setup.
Conclusion
In today's digital landscape, securing your DNS infrastructure is not just an option—it's a necessity. By implementing robust DNS security measures, you can protect your organization from a wide range of threats, ensure the continuity of your online services, and maintain the trust of your customers and partners.
Remember that DNS security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, regular updates, and a commitment to staying ahead of emerging threats. By following the best practices outlined in this article, leveraging advanced security tools, and keeping your team well-trained, you can build a resilient DNS infrastructure that forms a solid foundation for your overall cybersecurity strategy.
As you move forward with strengthening your DNS security:
- Regularly assess your DNS infrastructure for vulnerabilities
- Stay informed about the latest DNS security trends and threats
- Continuously refine your DNS security policies and procedures
- Invest in advanced DNS security solutions that align with your organization's needs
- Foster a culture of security awareness throughout your organization
Take the next step in securing your DNS infrastructure by leveraging WebSolutionMaster for maintaining your DNS records. Our advanced platform offers robust security features, real-time monitoring, and expert support to ensure your DNS remains protected against evolving threats. Don't leave your digital foundation vulnerable—trust WebSolutionMaster to safeguard your online presence and keep your business running smoothly.
Prioritizing DNS security and taking proactive measures to protect this critical component of your digital infrastructure, you'll be well-positioned to navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape and ensure the long-term success of your online presence.
Useful References
- ICANN: DNS Security
- OWASP: DNS Security Best Practices
- Cloudflare Learning Center: DNS Security
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): DNS Security Guidelines
- Google’s Public DNS
- DNSSEC Deployment Initiative
- RFC 4033: DNS Security Introduction and Requirements
- BIND Documentation
- Splunk DNS Analytics
- ZDNet: Preventing DNS Attacks





