
Implementing Error Handling in a Next.js Application
Error handling is a critical aspect of web development, ensuring a smooth user experience and easier debugging. In the context of Next.js, a popular React framework for building server-side rendered and statically generated web applications, effective error handling is key to creating robust and user-friendly applications. This article will guide you through the steps to implement comprehensive error handling in a Next.js application.
Understanding Next.js Error Handling
Next.js provides built-in error handling capabilities, including a default error page (_error.js) and the ability to create custom error pages. However, to handle errors effectively, one must understand both client-side and server-side error handling in a Next.js application.
Default Error Page
Next.js automatically uses the _error.js page to handle errors. This page is used both for server-side errors (like a failed server-side data fetching) and client-side errors. To customize it, you just need to create an _error.js file in the pages directory.
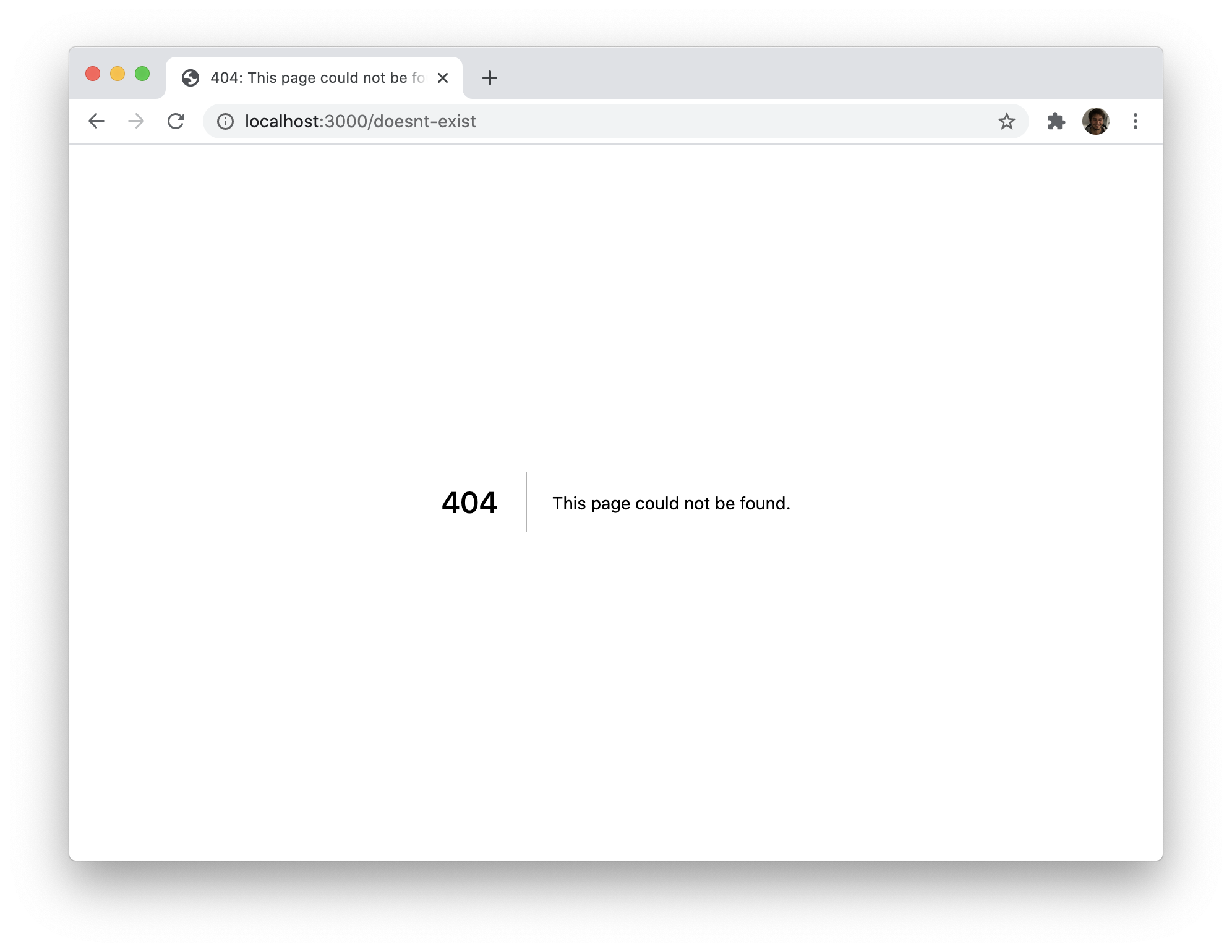
Creating a Custom Error Page
To create a custom error page, you should:
- Create a
_error.jsfile inside thepagesfolder. - Export a React component as default.
- Use the
statusCodeprop to display different messages or layouts for different HTTP status codes.
Example:
function Error({ statusCode }) {
return (
<p>
{statusCode
? `An error ${statusCode} occurred on the server`
: "An error occurred on the client"}
</p>
);
}
Error.getInitialProps = ({ res, err }) => {
const statusCode = res ? res.statusCode : err ? err.statusCode : 404;
return { statusCode };
};
export default Error;
Handling Server-Side Errors
Server-side errors in Next.js often occur during data fetching in functions like getServerSideProps or getStaticProps. To handle these errors:
- Use try-catch blocks within these functions.
- Log the errors for server-side debugging.
- Optionally, pass error information to the page's props to display an error message.
Example:
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
try {
const data = await fetchData();
return { props: { data } };
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching data:", error);
return { props: { error: "Error fetching data" } };
}
}
Handling Client-Side Errors
Client-side error handling in Next.js revolves around handling errors in React components or when using client-side data fetching methods like fetch.
- Use React's error boundaries to catch and handle errors in components.
- For data fetching, use try-catch blocks and manage error states.
Example of an Error Boundary in React:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// Log the error to an error reporting service
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// Render any custom fallback UI
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
Logging and Monitoring
Implement logging and monitoring to track and analyze errors. Tools like Sentry, LogRocket, or custom logging solutions can be integrated into your Next.js application to capture both server-side and client-side errors.
Testing Error Scenarios
Ensure that you test error scenarios in your application. This includes simulating server failures, client-side exceptions, and network issues to verify that your application handles these gracefully.
User-Friendly Error Messages
Always display user-friendly error messages and provide ways for the user to navigate back to a functional state, such as a link to the home page or a retry button for failed operations.
Async Error Handling in Hooks and Components
When using hooks like useState and useEffect in your Next.js application, it's important to handle asynchronous operations and their potential errors carefully.
For useEffect, if you're fetching data or performing any async operation:
- Use a try-catch block inside the async function.
- Set state variables to handle loading and error states.
Example:
const MyComponent = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchData = async () => {
setLoading(true);
try {
const response = await fetch("/api/data");
const result = await response.json();
setData(result);
} catch (err) {
setError(err.message);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
};
fetchData();
}, []);
if (loading) return <div>Loading...</div>;
if (error) return <div>Error: {error}</div>;
return <div>{/* Render your data */}</div>;
};
Handling API Errors in Next.js API Routes
If you're using Next.js API routes, handling errors is also crucial. It's a good practice to create a consistent structure for error responses. Use try-catch blocks inside API routes, and return appropriate HTTP status codes along with error messages.
Example:
export default async function handler(req, res) {
try {
// Perform API logic
res.status(200).json({ data: "Success" });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal Server Error" });
}
}
Use Middleware for Error Handling
Consider using middleware for error handling in your Next.js application. Middleware can help you manage errors more effectively by creating a centralized error handling mechanism. This can be particularly useful for server-side logic and API routes.
Custom Hooks for Reusable Error Handling
Create custom hooks for handling errors in reusable components or functions. This approach helps maintain clean code and promotes the DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principle.
Example of a custom hook for data fetching:
const useFetch = (url) => {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchData = async () => {
setLoading(true);
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
const result = await response.json();
setData(result);
} catch (err) {
setError(err.message);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
};
fetchData();
}, [url]);
return { data, loading, error };
};
Client-Side Routing Errors
Handle errors in client-side routing effectively. For example, if you're using next/router to navigate programmatically, ensure that you handle scenarios where the navigation might fail or the destination route might not exist.
Environment-Specific Error Handling
Implement environment-specific error handling. For instance, you might want to show detailed error messages or stack traces in a development environment but not in production. You can use environment variables to toggle this behavior.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuously monitor the errors your application encounters in production, and use the insights to improve your error handling strategies. Regularly updating and refining your error handling approach is key to maintaining a resilient and reliable Next.js application.
Following these practices and incorporating robust error handling strategies, you ensure that your Next.js application can gracefully handle unexpected situations, providing a better experience for both developers and users.
Conclusion
Effective error handling in Next.js involves understanding the framework's built-in capabilities and complementing them with additional practices like custom error pages, server-side and client-side error management, error boundaries, logging, monitoring, and user-friendly error messaging. By implementing these practices, you can create a more resilient and user-friendly Next.js application.





